-
Thermal Desorption, Vibrational Spectroscopic, and DFT Computational Studies of the Complex Manganese Borohydrides Mn(BH4)2 and [Mn(BH4)4]2−
G. Severa, H. Hagemann, M. Longhini, J.W. Kaminski, T.A. Wesolowski and C.M. Jensen
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 114 (36) (2010), p15516-15521


DOI:10.1021/jp101675q | unige:14754 | Abstract | Article HTML | Article PDF

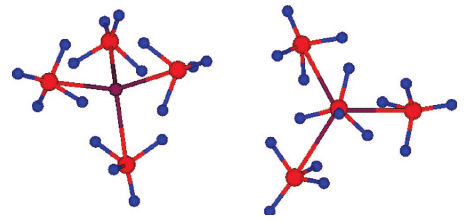
The mechanochemical reaction of LiBH4¬†with MnCl2¬†produces the neutral complex Mn(BH4)2. Thermal desorption studies show that the mechanochemical reaction of NaBH4¬†with MnCl2produces a different species, apparently Na2Mn(BH4)4, that undergoes dehydrogenation of a much lower weight percent H at a ~20 ¬įC higher temperature than the neutral Mn(BH4)2. Vibrational spectroscopy also reveals that a complex manganese borohydride(s) in addition to Mn(BH4)2¬†are formed from the mechanochemical reactions. Analysis of the vibrational spectra in conjunction with DFT calculations on a model Mn(BH4)42‚ąí¬†complex suggest bidentate binding of the [BH4]‚ąí¬†ligands to the Mn center in the anionic complex. The calculated highest frequencies of the B‚ąíH stretching modes (corresponding to the ‚Äúfree‚ÄĚ B‚ąíH bonds) agree well with the experimental frequencies and support the presence of this structural feature.